Paper Authors and Title
Caitriona McGearty and Daniela Maslovska (Technological University Dublin), Louise Kearney, Tao Zhang, “The Impact of Different Sustainable Extraction Approaches on the Phytochemical Profiles and Antimicrobial Activities of the Extracts of Cinnamomum cassia and Illicium verum”
Abstract
Background
Cinnamomum cassia and Illicium verum are ancient spices which date back to 3000BC, and both have been used in Traditional Chinese medicine, contemporary medicine in East Asian countries and being more often used in the culinary industry as spices. The pharmacological and nutraceutical properties of these spices have been demonstrated, including antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, cardiovascular-disease-reducing and lipid-lowering effects. It has also been of interest in the cosmetic industry.
Aims
This study was to evaluate the impact of the different sustainable extraction methods on the phytochemical and the related antimicrobial activity of the extracts of Cinnamomum cassia and Illicium verum.
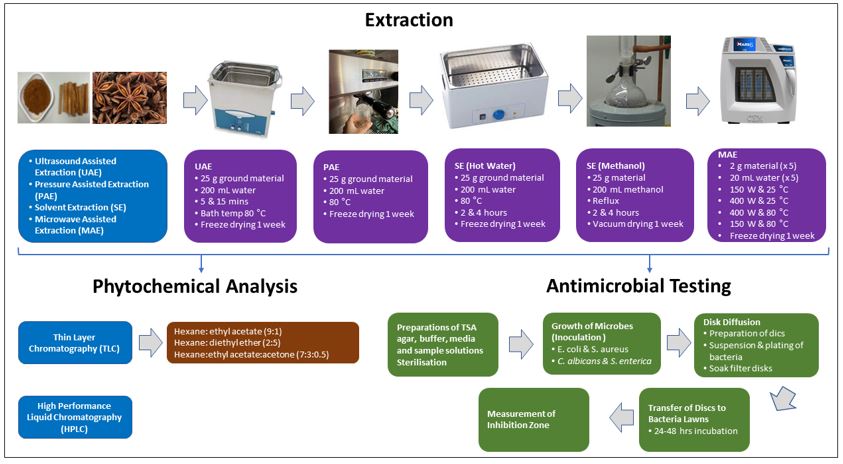
Methods
Extraction methods were chosen as follows: ultrasound-assisted-extraction (UAE): 5 mins (1) and 15 mins (2), pressure-assisted-extraction (PAE, 3), hot-water-extraction (HWE, 4) and hot-methanol-extraction (HME, 5), maceration (6) and microwave-assisted-extraction (MAE, 7). Different parameters (temperatures, power and time) were used. Extracts were subjected to phytochemical content analysis by thin-layer-chromatography, and the percentage yield of extraction was determined and compared by high-performance-liquid-chromatography. The antimicrobial assay (disc diffusion) was performed against E.coli & S.aureus (Cinnamomum cassia), and C.albicans & S.enterica (Illicium verum).
Results
Cinnamomum cassia extracts 1- 4 had inhibitory effects on S.aureus at 20% (ZOI 8.5-9.5 mm). However, extract 5 produced a ZOI of 6 mm at 2% indicating a 20% concentration would have been superior to extraction methods 1-4 if it was performed in this study. There was no activity against E.coli. Illicium verum extracts showed some activities against C.albicans compared to S.enterica; however, overall inhibition activity was quite low.
Poster
Download and view Caitriona McGearty and Daniela Maslovska’s poster.